The Looming Crisis: Addressing the Psychiatrist Shortage in America
The United States is facing a significant and growing crisis: a severe psychiatrist shortage. This shortage is impacting access to mental healthcare for millions of Americans, exacerbating existing mental health challenges, and contributing to a nationwide decline in overall well-being. Understanding the causes, consequences, and potential solutions to this psychiatrist shortage is crucial for policymakers, healthcare providers, and individuals alike.
Understanding the Scope of the Psychiatrist Shortage
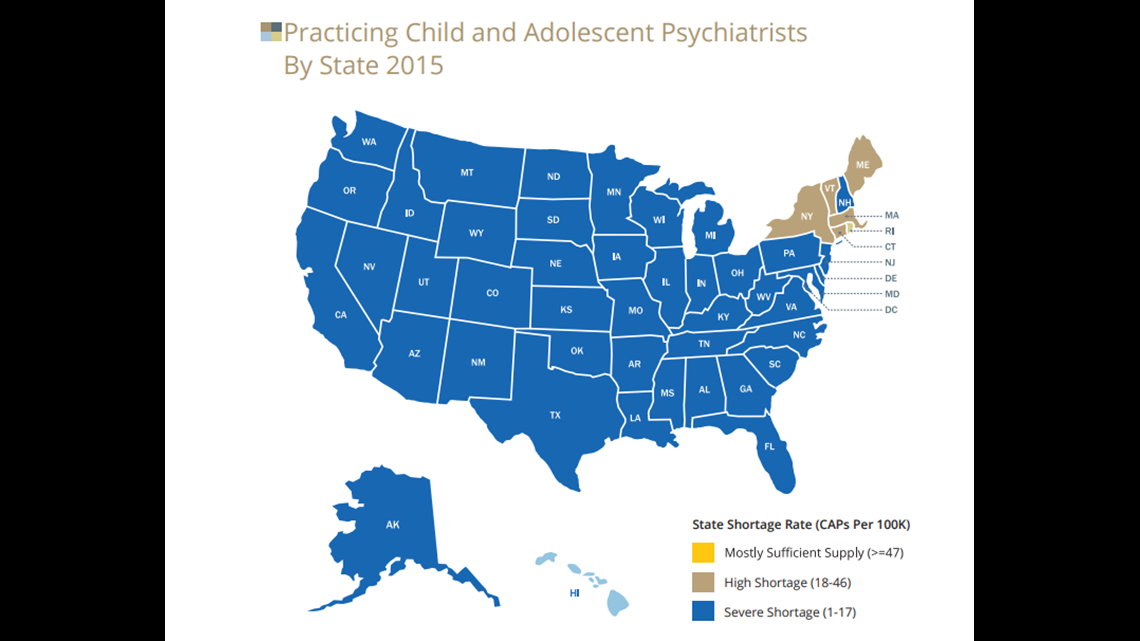
The psychiatrist shortage isn’t a new phenomenon, but it’s rapidly intensifying. According to the Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA), a significant portion of the U.S. is designated as a mental health professional shortage area (HPSA). This means that there are not enough psychiatrists to meet the needs of the population. Estimates vary, but projections suggest a shortfall of thousands of psychiatrists in the coming years. This deficit impacts both urban and rural communities, although rural areas often face even greater challenges due to limited resources and infrastructure. The psychiatrist shortage is particularly acute for child and adolescent psychiatry, leaving many young people without access to critical mental healthcare services.
Contributing Factors to the Psychiatrist Shortage
Several factors contribute to the current psychiatrist shortage. One of the primary drivers is the aging workforce. A significant percentage of practicing psychiatrists are nearing retirement age, and the number of new psychiatrists entering the field isn’t keeping pace. This imbalance creates a gap in the workforce that is difficult to fill. Furthermore, the demanding nature of psychiatric practice, including long hours, high stress levels, and complex patient cases, can deter medical students from choosing psychiatry as their specialty. [See also: The Impact of Burnout on Healthcare Professionals]
Another contributing factor is the inadequate reimbursement rates for mental health services compared to other medical specialties. This disparity can make psychiatry less financially attractive to medical students burdened with student loan debt. Additionally, the stigma surrounding mental illness can discourage both patients from seeking treatment and medical professionals from specializing in psychiatry. Efforts to reduce stigma are essential to encouraging more individuals to pursue careers in mental healthcare.
Geographic Disparities
The psychiatrist shortage is not evenly distributed across the country. Rural areas and underserved communities often experience the most severe shortages. These areas may lack the resources and infrastructure to attract and retain psychiatrists. Factors such as lower salaries, limited professional opportunities, and a lack of cultural amenities can make it difficult to recruit psychiatrists to these regions. Telepsychiatry offers a potential solution to address geographic disparities by providing remote access to mental healthcare services. [See also: Telehealth and the Future of Mental Healthcare]
Consequences of the Psychiatrist Shortage
The consequences of the psychiatrist shortage are far-reaching and affect individuals, families, and communities. One of the most immediate impacts is reduced access to mental healthcare. Individuals struggling with mental health conditions may face long wait times for appointments, limited treatment options, and difficulty finding a psychiatrist who accepts their insurance. This lack of access can lead to delays in diagnosis and treatment, worsening mental health outcomes and increasing the risk of hospitalization, substance abuse, and suicide.
The psychiatrist shortage also places a strain on other healthcare providers, such as primary care physicians and emergency room staff, who are often forced to fill the gap in mental healthcare services. These providers may not have the specialized training or resources to effectively treat complex mental health conditions, leading to suboptimal care. Moreover, the shortage can contribute to increased healthcare costs, as individuals with untreated mental health conditions may require more intensive and expensive medical interventions.
Impact on Specific Populations
Certain populations are particularly vulnerable to the effects of the psychiatrist shortage. Children and adolescents with mental health disorders may experience developmental delays, academic difficulties, and increased risk of substance abuse and suicide. Veterans with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and other mental health conditions may face barriers to accessing timely and effective treatment. Individuals with co-occurring mental health and substance use disorders may struggle to find integrated care that addresses both conditions simultaneously. Addressing the specific needs of these vulnerable populations is crucial to mitigating the impact of the psychiatrist shortage.
Potential Solutions to the Psychiatrist Shortage
Addressing the psychiatrist shortage requires a multifaceted approach that involves increasing the supply of psychiatrists, improving access to mental healthcare, and reducing the stigma surrounding mental illness. One potential solution is to expand residency programs and increase funding for psychiatric education. This would help to train more psychiatrists and ensure that they are adequately prepared to meet the needs of the population. Loan repayment programs and scholarships can also incentivize medical students to choose psychiatry as their specialty. [See also: The Role of Medical Education in Addressing Healthcare Shortages]
Another strategy is to expand the use of telepsychiatry, which can improve access to mental healthcare in rural areas and underserved communities. Telepsychiatry allows psychiatrists to provide remote consultations, diagnoses, and treatment through video conferencing and other technologies. This can help to overcome geographic barriers and reduce wait times for appointments. Furthermore, integrating mental healthcare into primary care settings can improve access to early intervention and prevention services. Collaborative care models, which involve primary care physicians and mental health specialists working together, can provide comprehensive and coordinated care for patients with mental health conditions.
Policy and Advocacy
Policy changes and advocacy efforts are also essential to addressing the psychiatrist shortage. Increasing reimbursement rates for mental health services can make psychiatry more financially attractive to medical students and encourage more psychiatrists to accept insurance. Enacting parity laws that require insurance companies to cover mental health services at the same level as physical health services can improve access to care and reduce disparities. Additionally, public awareness campaigns can help to reduce the stigma surrounding mental illness and encourage more individuals to seek treatment. Advocacy organizations play a crucial role in raising awareness about the psychiatrist shortage and advocating for policies that support mental healthcare access.
The Future of Mental Healthcare
The psychiatrist shortage presents a significant challenge to the future of mental healthcare in the United States. However, by implementing comprehensive strategies to increase the supply of psychiatrists, improve access to care, and reduce stigma, we can work towards a future where all Americans have access to the mental healthcare they need. This requires a collaborative effort from policymakers, healthcare providers, educators, and community organizations. Investing in mental healthcare is an investment in the health and well-being of our nation. The increasing awareness of the psychiatrist shortage and its impact is a crucial first step towards meaningful change.
Furthermore, technological advancements offer promising solutions. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are being explored to assist in diagnosis and treatment planning, potentially freeing up psychiatrists to focus on more complex cases. Digital mental health platforms can provide accessible and affordable support, particularly for individuals in underserved areas. [See also: The Ethical Considerations of AI in Mental Healthcare]
Conclusion
The psychiatrist shortage is a complex and pressing issue that demands immediate attention. The consequences of inaction are severe, impacting individuals, families, and communities across the nation. By understanding the contributing factors, consequences, and potential solutions, we can work together to address this crisis and ensure that all Americans have access to the mental healthcare they need to thrive. The time to act is now. The future of mental healthcare depends on it.