Config Firewall: A Comprehensive Guide to Securing Your Network
In today’s interconnected world, network security is paramount. A firewall acts as the first line of defense, meticulously examining incoming and outgoing network traffic and blocking anything that doesn’t match the configured security policies. Understanding how to config firewall settings correctly is crucial for protecting your data and systems from unauthorized access and malicious attacks. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of firewall configuration, covering essential concepts and practical steps to enhance your network’s security posture. We will explore different types of firewalls, configuration methods, and best practices to help you effectively manage and config firewall settings for optimal protection.
Understanding Firewalls
What is a Firewall?
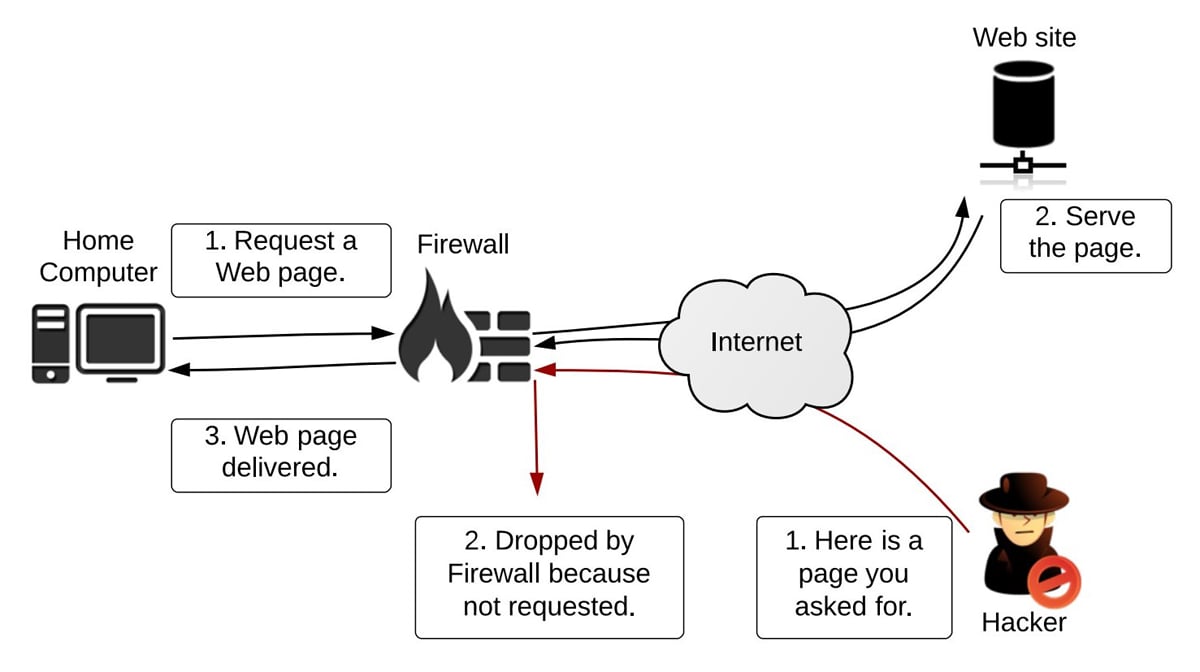
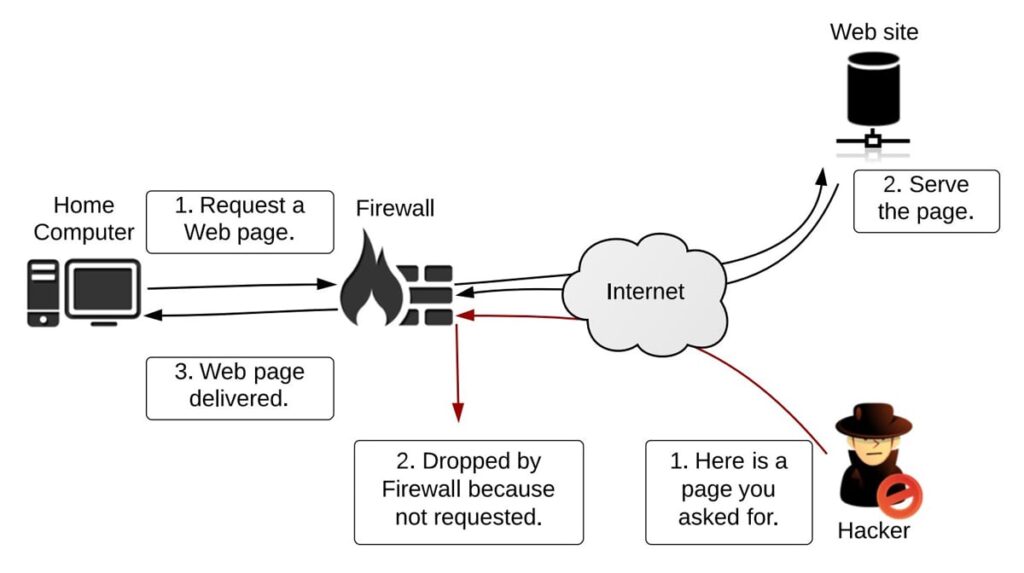
At its core, a firewall is a network security system that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. It acts as a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks, such as the internet. By analyzing network packets, a firewall can identify and block malicious traffic, preventing unauthorized access to your systems.
Types of Firewalls
Firewalls come in various forms, each with its own strengths and weaknesses:
- Packet Filtering Firewalls: These firewalls examine individual packets and compare them against a set of rules. They are relatively simple and fast but offer limited protection against sophisticated attacks.
- Stateful Inspection Firewalls: These firewalls track the state of network connections, providing more comprehensive protection than packet filtering firewalls. They analyze packets in the context of ongoing sessions, making it harder for attackers to bypass security measures.
- Proxy Firewalls: These firewalls act as intermediaries between clients and servers, masking the internal network’s IP addresses and providing an additional layer of security. They can also perform content filtering and caching.
- Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs): NGFWs combine traditional firewall features with advanced capabilities such as intrusion prevention, application control, and deep packet inspection. They offer a more holistic approach to network security.
Key Firewall Configuration Concepts
Rules and Policies
Firewall configuration revolves around defining rules and policies that dictate how network traffic is handled. These rules specify criteria such as source and destination IP addresses, ports, and protocols. When a network packet matches a rule, the firewall takes the specified action, such as allowing or denying the traffic. Proper configuration of these rules is vital to effectively config firewall settings.
Zones and Interfaces
Firewalls often use zones to group network interfaces with similar security requirements. For example, you might have a zone for your internal network, a zone for your DMZ (demilitarized zone), and a zone for the internet. By assigning interfaces to zones, you can apply different security policies to different parts of your network.
Network Address Translation (NAT)
NAT is a technique used to translate IP addresses. Firewalls often use NAT to hide the internal IP addresses of devices on your network from the outside world. This enhances security by making it more difficult for attackers to target specific devices.
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
VPNs create secure connections between networks or devices over the internet. Firewalls can be configured to support VPNs, allowing remote users to securely access your network resources. [See also: VPN Configuration Best Practices]
How to Config Firewall: Step-by-Step Guide
Planning Your Firewall Configuration
Before you start configuring your firewall, it’s essential to plan your approach. Consider the following factors:
- Network Topology: Understand the layout of your network, including the number of devices, subnets, and zones.
- Security Requirements: Identify the specific security threats you need to protect against.
- Traffic Patterns: Analyze the types of network traffic that flow through your network.
- Application Requirements: Determine which applications need to be allowed through the firewall.
Accessing the Firewall Configuration Interface
The process for accessing the firewall configuration interface varies depending on the firewall vendor and model. Common methods include:
- Web-based Interface: Most firewalls provide a web-based interface that can be accessed through a web browser.
- Command-Line Interface (CLI): Some firewalls offer a CLI that can be accessed through a terminal emulator.
- Dedicated Management Software: Some vendors provide dedicated management software for configuring and monitoring their firewalls.
Configuring Basic Firewall Settings
Once you have accessed the firewall configuration interface, start by configuring the basic settings:
- Set the Firewall’s IP Address: Assign a unique IP address to the firewall.
- Configure the Default Gateway: Specify the IP address of the default gateway.
- Set the DNS Servers: Configure the DNS servers that the firewall will use to resolve domain names.
- Enable Logging: Enable logging to track network traffic and security events.
Creating Firewall Rules
Creating firewall rules is the core of config firewall. Follow these steps:
- Define the Rule Name: Give the rule a descriptive name.
- Specify the Source and Destination IP Addresses: Enter the source and destination IP addresses or network ranges.
- Select the Protocol: Choose the protocol (e.g., TCP, UDP, ICMP).
- Specify the Ports: Enter the source and destination ports.
- Choose the Action: Select the action to take (e.g., allow, deny, reject).
- Enable Logging: Enable logging for the rule to track traffic that matches the rule.
Testing Your Firewall Configuration
After configuring your firewall, it’s crucial to test your configuration to ensure that it’s working as expected. Use tools like `ping`, `traceroute`, and `nmap` to test network connectivity and identify any issues. Verify that the firewall is blocking unauthorized traffic and allowing authorized traffic. This testing phase is crucial to ensure the effectiveness of your config firewall setup.
Firewall Best Practices
Principle of Least Privilege
Apply the principle of least privilege when configuring firewall rules. Only allow the minimum amount of network traffic necessary for applications to function correctly. This minimizes the attack surface and reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
Regularly Review and Update Firewall Rules
Firewall rules should be reviewed and updated regularly to reflect changes in your network environment and security requirements. Remove any rules that are no longer needed and update existing rules as necessary. Keeping your ruleset current is a key aspect of maintaining a properly config firewall.
Keep Your Firewall Software Up to Date
Firewall vendors regularly release updates to address security vulnerabilities and improve performance. It’s essential to keep your firewall software up to date to protect against the latest threats.
Monitor Firewall Logs
Regularly monitor firewall logs to identify suspicious activity and potential security breaches. Analyze the logs to understand traffic patterns and identify areas where your firewall configuration can be improved. This proactive monitoring is essential for effective config firewall management.
Implement Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS)
Consider implementing IDS/IPS to provide an additional layer of security. IDS/IPS can detect and prevent malicious activity that bypasses the firewall. [See also: Integrating IDS/IPS with Your Firewall]
Advanced Firewall Configuration Techniques
Application Control
Application control allows you to control which applications are allowed to run on your network. This can help prevent users from running unauthorized applications that could pose a security risk. NGFWs often include advanced application control features.
Deep Packet Inspection (DPI)
DPI allows the firewall to inspect the contents of network packets, not just the headers. This can help identify and block malicious traffic that is hidden within legitimate traffic. NGFWs utilize DPI to provide enhanced security.
Geolocation Filtering
Geolocation filtering allows you to block traffic from specific countries or regions. This can be useful for preventing attacks from known sources of malicious activity.
Troubleshooting Common Firewall Issues
Connectivity Problems
If you are experiencing connectivity problems after configuring your firewall, check the following:
- Firewall Rules: Verify that the firewall rules are allowing the necessary traffic.
- DNS Configuration: Ensure that the DNS servers are configured correctly.
- NAT Configuration: Check the NAT configuration to ensure that it is not blocking traffic.
Performance Issues
If your firewall is causing performance issues, consider the following:
- Firewall Rules: Optimize your firewall rules to reduce the processing load.
- Hardware Resources: Ensure that your firewall has sufficient hardware resources (e.g., CPU, memory) to handle the network traffic.
- Software Updates: Install the latest software updates to improve performance.
Conclusion
Configuring a firewall is a critical step in securing your network. By understanding the key concepts, following best practices, and regularly monitoring your firewall, you can effectively protect your data and systems from unauthorized access and malicious attacks. Remember to plan your configuration carefully, test your settings thoroughly, and stay up-to-date on the latest security threats. The process to config firewall is an ongoing effort that requires vigilance and adaptation. By mastering the art of config firewall settings, you significantly enhance your network’s overall security posture.