Mucus When I Poop: Understanding the Causes, Symptoms, and When to Seek Help
Finding mucus when I poop can be alarming. While it’s often a normal bodily function, excessive or unusual mucus when I poop can indicate an underlying health issue. This article will explore the causes, symptoms, and when it’s crucial to seek medical attention if you notice mucus when I poop. We aim to provide clear, accurate, and informative guidance to help you understand this common concern.
What is Mucus and Why Is It in My Stool?
Mucus is a jelly-like substance produced throughout your body, including the digestive tract. Its primary function is to lubricate and protect the lining of your intestines, making it easier for stool to pass. The presence of a small amount of mucus when I poop is perfectly normal and usually goes unnoticed. This thin layer of mucus when I poop helps facilitate smooth bowel movements.
However, an increase in the amount of mucus when I poop, or changes in its color or consistency, can signal a problem. Understanding the potential reasons for this change is essential for maintaining your digestive health.
Common Causes of Mucus in Stool
Several factors can contribute to increased mucus when I poop. These range from mild dietary issues to more serious medical conditions. Here’s a breakdown of some common causes:
- Dietary Factors: Certain foods, particularly those high in fiber or dairy, can sometimes lead to increased mucus when I poop. Intolerances or sensitivities to specific foods can also play a role.
- Dehydration: Insufficient fluid intake can result in harder stools, which may irritate the intestinal lining and cause more mucus when I poop.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): IBS is a chronic condition that affects the large intestine. It can cause abdominal pain, bloating, gas, and changes in bowel habits, including increased mucus when I poop. [See also: Managing IBS Symptoms Naturally]
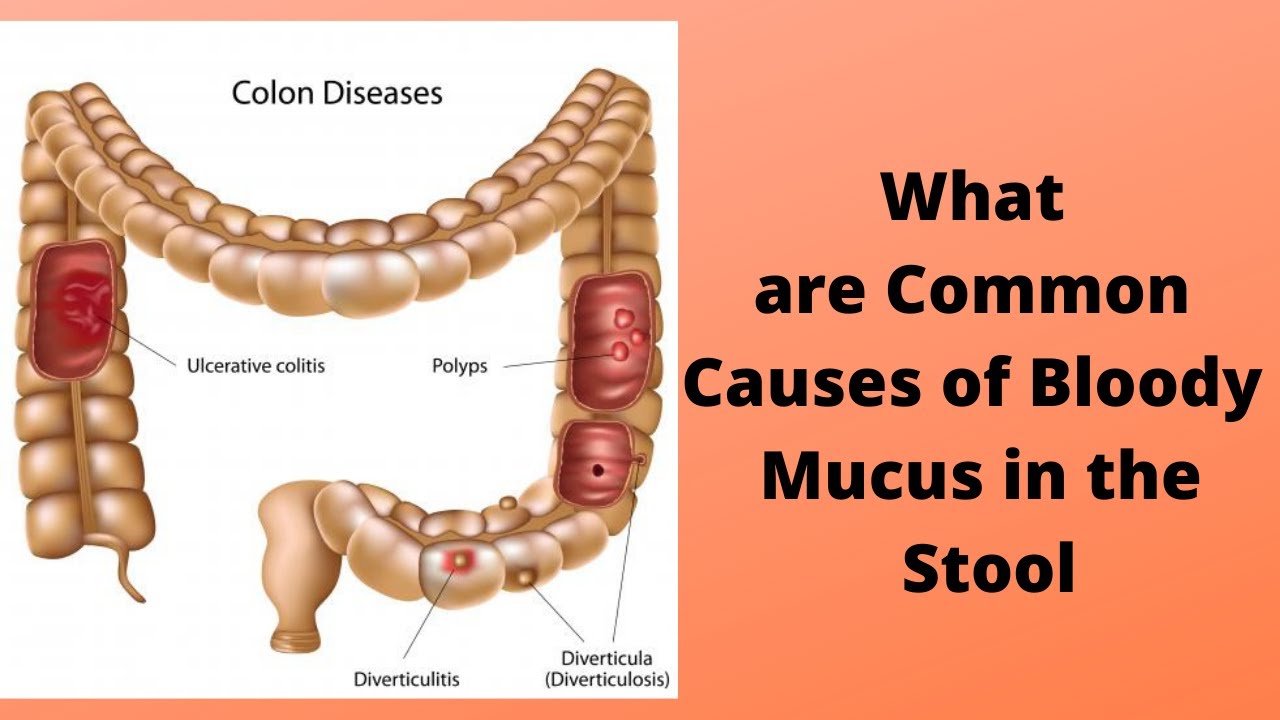
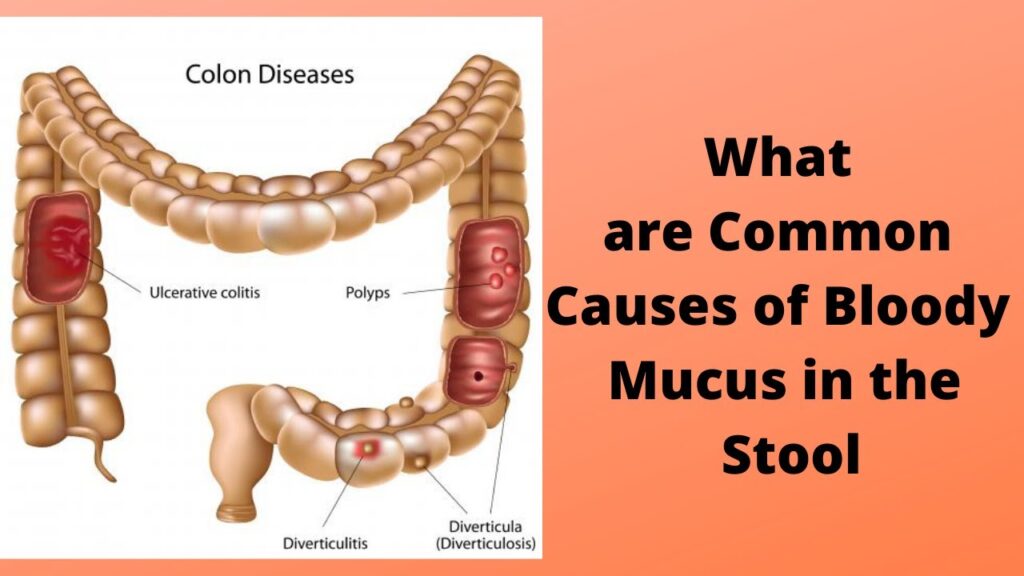
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): IBD, which includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, causes chronic inflammation of the digestive tract. This inflammation can lead to significant amounts of mucus when I poop, along with other symptoms like bloody stool and abdominal pain.
- Infections: Bacterial, viral, or parasitic infections in the digestive system can cause inflammation and increased mucus when I poop. These infections are often accompanied by diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and fever.
- Anal Fissures and Hemorrhoids: These conditions can cause irritation and inflammation in the anal area, leading to the production of mucus when I poop.
- Cystic Fibrosis: While primarily affecting the lungs, cystic fibrosis can also impact the digestive system, leading to abnormal mucus production.
Symptoms Associated with Mucus in Stool
The symptoms that accompany mucus when I poop can vary depending on the underlying cause. Some people may experience no other symptoms, while others may have a range of digestive issues. Common symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain or cramping
- Bloating and gas
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Changes in stool consistency
- Blood in the stool
- Urgent need to have a bowel movement
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
If you experience any of these symptoms along with excessive mucus when I poop, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While occasional mucus when I poop is usually not a cause for concern, certain situations warrant medical attention. You should see a doctor if you experience any of the following:
- Significant increase in the amount of mucus: If you notice a substantial change in the amount of mucus when I poop, it’s essential to get it checked out.
- Blood in the stool: Blood mixed with mucus when I poop can indicate a more serious condition, such as IBD or an infection.
- Persistent abdominal pain: Ongoing abdominal pain, especially when accompanied by other digestive symptoms, should be evaluated by a doctor.
- Unexplained weight loss: Weight loss without a clear reason can be a sign of an underlying medical condition.
- Fever: A fever along with digestive symptoms may indicate an infection.
- Changes in bowel habits: Significant changes in your bowel habits, such as persistent diarrhea or constipation, should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
- Mucus when I poop after starting a new medication: Some medications can affect your digestive system.
Diagnosis and Treatment
To determine the cause of increased mucus when I poop, your doctor may perform a physical exam and ask about your medical history and symptoms. They may also order the following tests:
- Stool Sample: A stool sample can help identify infections, parasites, or other abnormalities.
- Colonoscopy: A colonoscopy involves inserting a thin, flexible tube with a camera into the colon to visualize the lining of the large intestine. This can help detect inflammation, ulcers, or other abnormalities.
- Sigmoidoscopy: Similar to a colonoscopy, but it only examines the lower part of the colon.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can help detect signs of inflammation or infection.
- Imaging Tests: Imaging tests, such as CT scans or MRIs, may be used to visualize the digestive tract and identify any structural abnormalities.
Treatment for mucus when I poop will depend on the underlying cause. Some common treatment options include:
- Dietary Changes: Adjusting your diet to avoid trigger foods or increase fiber intake can help manage symptoms.
- Medications: Depending on the cause, your doctor may prescribe medications to treat infections, reduce inflammation, or manage IBS symptoms. For example, antibiotics will treat bacterial infections. Anti-inflammatory drugs can help with IBD.
- Probiotics: Probiotics can help restore the balance of bacteria in the gut and improve digestive health.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to treat underlying conditions, such as severe IBD or anal fissures.
Home Remedies and Prevention
In addition to medical treatment, several home remedies and lifestyle changes can help manage mucus when I poop and prevent it from recurring:
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help soften stools and reduce irritation in the digestive tract.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: A diet rich in fiber, fruits, and vegetables can promote healthy digestion.
- Identify and Avoid Trigger Foods: Keep a food diary to identify any foods that may be contributing to your symptoms.
- Manage Stress: Stress can exacerbate digestive issues. Practice stress-reducing techniques, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Consider Probiotics: Probiotic supplements or foods like yogurt and kefir can help improve gut health.
The Psychological Impact of Digestive Issues
Experiencing digestive issues like increased mucus when I poop can have a significant impact on your mental and emotional well-being. The discomfort, uncertainty, and potential embarrassment associated with these symptoms can lead to anxiety, stress, and even depression. It’s essential to acknowledge these psychological effects and seek support when needed.
Talking to a therapist or counselor can help you cope with the emotional challenges of managing a chronic digestive condition. Support groups can also provide a sense of community and understanding. Remember, taking care of your mental health is just as important as addressing the physical symptoms.
Living with Chronic Digestive Conditions
For individuals living with chronic digestive conditions like IBS or IBD, managing symptoms like mucus when I poop becomes an ongoing process. Learning to navigate daily life while managing these conditions requires a combination of medical treatment, lifestyle adjustments, and self-care strategies.
Developing a strong support system is crucial. This may include family, friends, healthcare professionals, and online communities. Sharing your experiences and learning from others can help you feel less alone and more empowered to manage your condition. [See also: Building a Strong Support System for Chronic Illness]
Conclusion
Finding mucus when I poop can be concerning, but it’s often a normal occurrence. However, if you notice a significant increase in the amount of mucus when I poop, or if it’s accompanied by other symptoms like blood in the stool, abdominal pain, or changes in bowel habits, it’s essential to seek medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications and improve your overall quality of life. Remember that proper hydration, a balanced diet, and stress management can play a significant role in maintaining healthy digestion and reducing the likelihood of excessive mucus when I poop. Don’t hesitate to consult with a healthcare professional to address any concerns and receive personalized guidance.